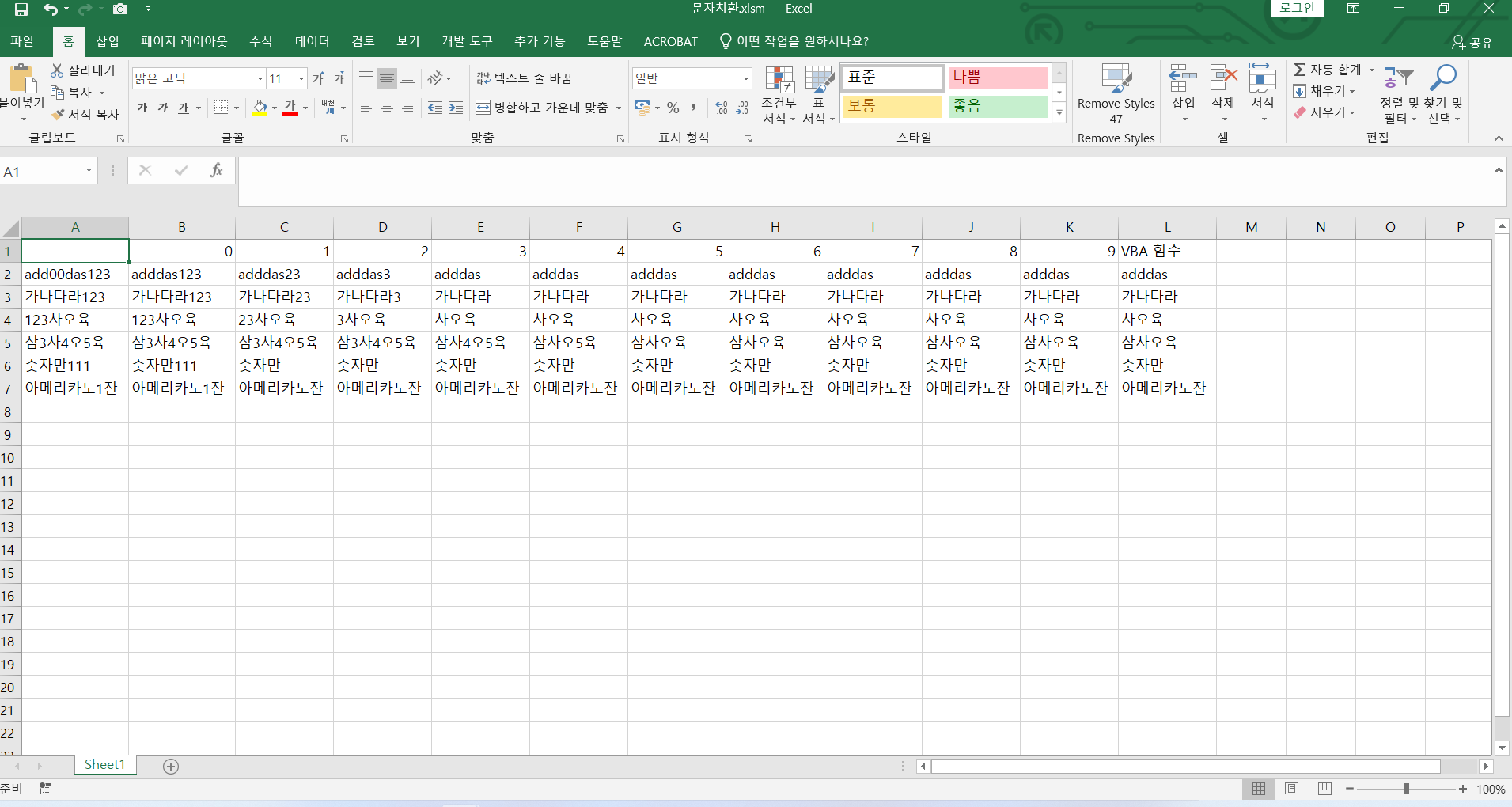
Functions Visual Basic for Applications
Abs(x)
The absolute value of x
Atn(x)
Inverse tangent of x. Other inverse functions may be computed using trigonometric identities such as Arcsin(X) = Atn(X / Sqr(-X*X + 1)). For more information, search Visual Basic Help for derived math functions
Cos(x)
The cosine of x, where x is expressed in radians
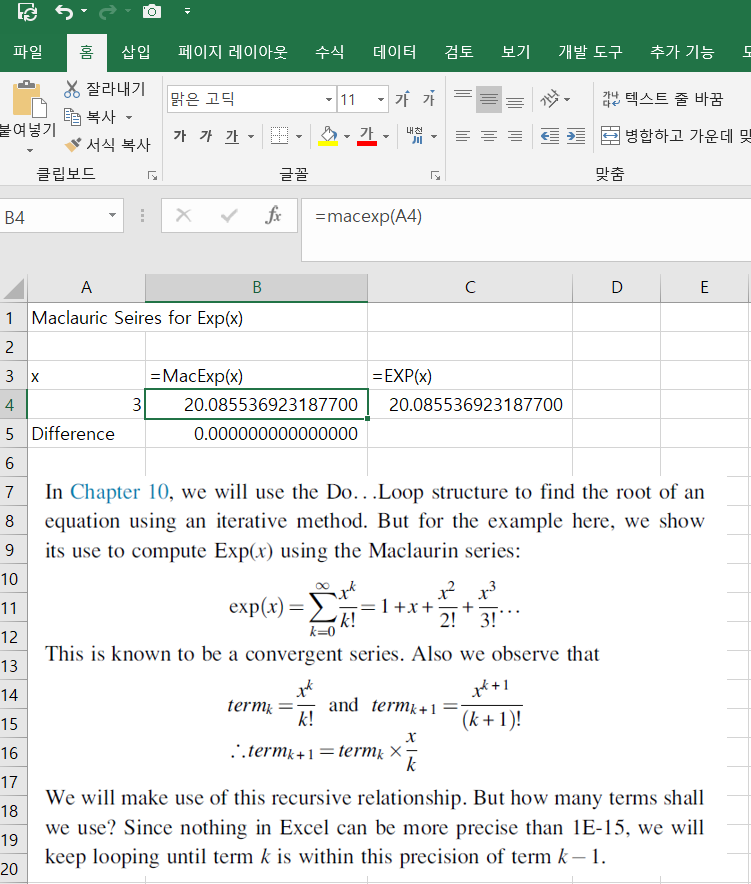
Exp(x)
The value e^x
Fix(x)
Returns the integer portion of x. If x is negative, Fix returns the first negative integer greater than or equal to x; for
example, Fix(-7.3) returns -7. See also Int
Int(x)
Returns the integer portion of x. If x is negative, Int returns the first negative integer less than or equal to x; for
example, Int(-7.3) returns -8. See also Fix
Log(x)
The value of the natural logarithm of x. Note how this differs from the worksheet function with the same name that, without a second argument, returns the logarithm to base 10. In VBA, the logarithm of x to base n may be
found using the statement y = Log(x)/Log(n)
Mod
In Visual Basic, this is an operator, not a function, but it is similar to the worksheet MOD function. It is used in the
form number Mod divisor and returns the remainder of number divided by divisor after rounding floating-point
values to integers. The worksheet function and the VBA operator return different values when the number and
divisor have opposite signs; see Help for details
Rnd(x)
Returns a random number between 0 and 1
Sgn(x)
Returns -1, 0, or 1 depending on whether x has a negative, zero, or positive value
Sin(x)
The sine of x, where x is expressed in radians
Sqr(x)
Square root of x
Tan(x)
The tangent of x